About Newt
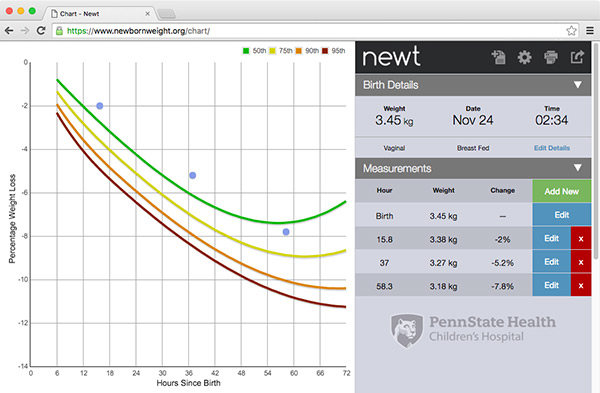
Newt® is the first tool created that allows pediatric healthcare providers and parents to see how a newborn’s weight during the first month following childbirth compares with a large sample of newborns. Using a research sample of birth weights from more than 160,000 newborns, the tool uses a nomogram to plot a baby’s weight percentile at any given time in the first month following birth compared with the research population. The results can be used for early identification of infants on a trajectory for greater weight loss, poor weight gain, and related complications.
The tool was developed by Dr. Ian Paul, M.D., M.Sc. at Penn State Hershey Children’s Hospital, Dr. Valerie Flaherman, MD, MPH at University of California San Francisco, Pediatrics, and Eric W. Schaefer, MS at Penn State College of Medicine, as well as with contributions from partners at Kaiser Permanente Division of Research and others.
The Research
A cohort of 161,471 healthy, singleton newborns born at ≥36 weeks gestation at 14 Northern California Kaiser Permanente hospitals between 2009 and 2013 were included in the research that generated the Newt nomograms. Data were extracted from the birth hospitalization regarding delivery mode, feeding type, and weights from electronic records. A total of 108,932 newborns had weights recorded while exclusively breastfeeding with 83,446 delivered vaginally and 25,486 delivered by Cesarean. An additional 7,075 were exclusively formula fed and had weights recorded with 4,525 delivered vaginally and 2,550 delivered by Cesarean section. Weights obtained after a newborn had been fed both breast milk and formula during the birth hospitalization were not included in this research. For each exclusive feeding type, quantile regression was used separately for each delivery mode to estimate the 50th (median), 75th, 90th and 95th percentiles of weight loss as a function of time after birth. For newborns fed breast milk, percentiles were estimated from 6 through 72 and 96 hours of age for those delivered vaginally and via Cesarean section, respectively. Given the smaller sample size for exclusively formula fed newborns, these nomograms extend through 48 hours for vaginally delivered newborns and 72 hours for those delivered via Cesarean section.
This research was funded by grant R40 MC 26811 through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration, Maternal and Child Health Research Program.
The Team
Ian M. Paul, M.D., M.Sc.

Ian M. Paul is the University Professor of Pediatrics and Public Health Sciences and Chief of the Division of Academic General Pediatrics at the Penn State College of Medicine. He is also Vice Chair of Faculty Affairs at Penn State Children’s Hospital.
Dr. Paul is a pediatrician and clinical and health services researcher with principal interests in a) primary preventive interventions for newborns, infants, and families and b) clinical therapeutics for children. His research focuses on these two areas with the largest current project focusing on promoting multigenerational cardiovascular health during the pregnancy and postpartum period for mothers and during early life for their offspring. This project is supported by the National Institutes of Health through the National Heart, Lung and Blood institute. This research extends his prior successful study on the prevention of childhood obesity through home-based interventions delivered to parents of infants.
Dr. Paul is or has been a co-investigator on numerous federally funded projects related to co-parenting, infant sleep, prevention of Shaken Baby Syndrome, prevention of adverse pregnancy outcomes, breastfeeding, and the treatment of asthma. In recognition of his contributions to the health of infants, mothers, and children in the United States, in 2019 he received the Director’s Award from the U.S. Health Resources & Services Administration’s Maternal and Child Health Bureau. Locally at Penn State, he received the Excellence in Career Mentoring Award in 2020. In 2022, he was honored with the Academic Pediatric Association’s Research Award.
Dr. Paul is also an internationally recognized expert on the pediatric treatment of the common cold and its symptoms having led numerous investigations related to cough/cold medications and antipyretics. A clinician as well, Dr. Paul has a thriving general pediatric practice where he provides medical care for children from birth through age 21 years.
Dr. Paul received his B.A. from Franklin and Marshall College (cum laude) with a major in Chemistry (with honors), received both graduate degrees (M.D. and M.Sc.) from The Penn State College of Medicine, and completed his pediatric residency at Duke University.
Valerie Flaherman, M.D., M.P.H.

Valerie Flaherman, MD, MPH, is Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology and Biostatistics at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF). She is an attending physician in the UCSF Newborn Nursery, where her research program focuses on optimizing preventive care during the birth hospitalization.
Eric Schaefer, MS

Eric is a biostatistician in the Department of Public Health Sciences at the Penn State University College of Medicine (Hershey, PA). He is a statistical consultant for a wide range of biomedical researchers at Penn State and he collaborates with clinical and health services researchers primarily in the Departments of Pediatrics, Surgery, and Public Health Sciences. He also supports the Division of Outcomes, Research and Quality and he has collaborated with social scientists at Dickinson College (Carlisle, PA). Eric provides statistical support for all phases of research, from study design and data management to expert analysis of data and dissemination of results. His current research interests include propensity scores, quantile regression, visualization, and computational statistics.
Eric joined Penn State in 2009. His previous professional experience includes 1 year as biostatistician at the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center, and 3 years as a research associate at the Center for Public Health Statistics at the University of Iowa. He holds a Master of Science degree in biostatistics from the University of Iowa and Bachelor of Science degrees from the University of Wisconsin-River Falls with majors in mathematics and computer systems.